 | HTML & XHTML: The Definitive Guide, 4th Edition |  |

Frame layout is similar to table layout. Using the <frameset> tag, you can arrange frames into rows and columns while defining their relative or absolute sizes.
The <frameset> tag lets you define a collection of frames and control their spacing and borders. Use the <frameset> tag to define a collection of frames and other framesets. Framesets also may be nested, allowing for a richer set of layout capabilities.
<frameset>
- Function:
Define a collection of frames
- Attributes:
BORDER
ONLOAD
BORDERCOLOR
ONUNLOAD
CLASS
ROWS
COLS
STYLE
FRAMEBORDER
TITLE
FRAMESPACING
ID
- End tag:
</frameset>; never omitted
- Contains:
frameset_content
- Used in:
html_content
Use the <frameset> tag in lieu of a <body> tag in the frame document. You may not include any other content except valid <head> and <frameset> content in a frame document. Combining frames with a conventional document containing a <body> section may result in unpredictable browser behavior.
The <frameset> tag has one required attribute: either cols or rows -- your choice. They define the size and number of columns (cols) or rows of either frames or nested framesets for the document window. Both attributes accept a quote-enclosed, comma-separated list of values that specify either the absolute (pixels) or relative (percentage or remaining space) width (for columns) or height (for rows) for the frames. The number of attribute values determines how many rows or columns of frames the browser will display in the document window.
As with tables, the browser will match the size you give a frameset as closely as possible. The browser will not, however, extend the boundaries of the main document window to accommodate framesets that would otherwise exceed those boundaries or fill the window with empty space if the specified frames don't fill the window. Rather, the browsers allocate space to a particular frame relative to all other frames in the row and column and resolutely fills the entire document window. (Did you notice that a frame document window does not have scrollbars?)
For example:
<frameset rows="150,300,150">
creates three rows of frames, each extending across the entire document window. The first and last frames are set to 150 pixels tall, the second to 300 pixels. In reality, unless the browser window is exactly 600 pixels tall, the browser automatically and proportionately stretches or compresses the first and last frames so that each occupies one quarter of the window space. The center row occupies the remaining half of the window space.
Frame row and column size values expressed as a percentage of the window dimensions are more sensible. For instance, the following example is effectively identical to the previous one:
<frameset rows="25%,50%,25%">
Of course, if the percentages don't add up to 100 percent, the browser automatically and proportionally resizes each row to make up the difference.
If you are like us, making things add up is not a strength. Perhaps some of the frame designers suffer the same difficulty, which would explain why they included the very nifty asterisk option for <frameset> rows and cols values. It tells the browser to size the respective column or row to whatever space is left over after putting adjacent frames into the frameset.
For example, when the browser encounters the following frame tag:
<frameset cols="100,*">
it makes a fixed-sized column 100 pixels wide, and then creates another frame column that occupies all of the remaining space in the frameset.
Here's a fancier layout example:
<frameset cols="10,*,10">
This one creates two very thin columns down the edges of the frameset and gives the remaining center portion to the middle column.
You may also use the asterisk for more than one row- or column-attribute value. In that case, the corresponding rows or columns equally divide the available space. For example:
<frameset rows="*,100,*">
creates a 100-pixel tall row in the middle of the frameset and equal-sized rows above and below it.
If you precede the asterisk with an integer value, the corresponding row or column gets proportionally more of the available space. For example:
<frameset cols="10%,3*,*,*">
creates four columns: the first column occupies 10 percent of the overall width of the frameset. The browser then gives the second frame 3/5 of the remaining space, and the third and the fourth are each given 1/5 of the remaining space.
Using asterisks (especially with the numeric prefix) makes it easy to divide up the remaining space in a frameset.
Be aware, too, that unless you explicitly tell it not to, the browser lets users manually resize the individual frame document's columns and rows, and hence change the relative proportions each frame occupies in their frames display. To prevent this, see the noresize attribute for the <frame> tag. the sidebar "<frame>"
The popular browsers provide attribute extensions that you may use to generally define and change the borders surrounding the frames in a frameset. The HTML 4 and XHTML standards prefer instead that you include these border-related display features via <style> tag attributes.
Both Internet Explorer and Netscape accept the frameborder attribute to disable or explicitly enable frame borders. (By default, every frame in a frameset as well as the frameset window itself is rendered with a 3D border; see Figure 11-1.) The two browsers' documentation disagree about the particular values for the frameborder attribute, but both acknowledge the other's conventions. Hence, setting the value of frameborder to 0 or no turns borders off (see Figure 11-2); 1 or yes turns borders on.
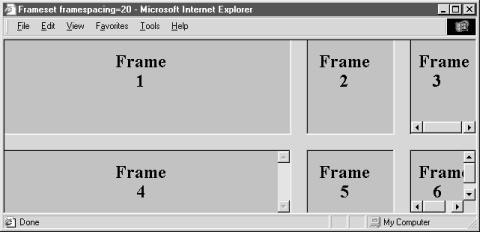
Internet Explorer and Netscape do disagree, however, as to how you may control the thickness of the borders. The latest version of Internet Explorer (Version 5) supports both the framespacing and border attributes, whose value is the number of pixels you want between frames (see Figure 11-3).
These attributes affect all frames and framesets nested within the current frameset as displayed by Internet Explorer. In practice, you should set it once on the outermost <frameset> to create a consistent border appearance for all of the frames in a single page.
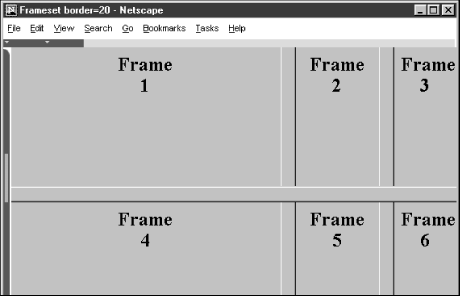
Netscape accepts only the border attribute to define the border width, with an integer value in pixels. Like Internet Explorer, Netscape lets you include the frameborder attribute with any <frameset> tag, affecting all nested frames and framesets. Unlike Internet Explorer, Netscape lets you include the border attribute only in the outermost <frameset>, ensuring that all frame borders are the same width within that <frameset>.
Since browsers ignore unsupported attributes, it is possible to define frame borders so that both browsers do the right thing. Just make sure to use the same framespacing and border values.
Finally, both Netscape and the latest version of Internet Explorer (Version 5) let you control the color of the frame borders using the bordercolor attribute (Figure 11-4). It accepts a color name or hexadecimal triple as its value. A complete list of color names and values can be found in Appendix G, "Color Names and Values".
Internet Explorer and Netscape, as standardized in HTML 4 and XHTML, support JavaScript-related event handlers that let your frame documents react when they are first loaded and when the frame window gets resized (onLoad); unloaded from the browser by the user (onUnload); when the window containing the frameset loses focus, such as when the user selects another window (onBlur); or when the frameset becomes the active window (onFocus). Included as <frameset> attributes, these event handlers take quote-enclosed lists of JavaScript commands and function calls as their value. For example, you might notify the user when all the contents have been loaded into their respective frames of a lengthy frameset:
<frameset onLoad="window.alert('Everything is loaded. You may now continue.')">These four attributes may also be used with the <body> tag. We cover JavaScript event handlers in more detail in Section 12.3.3, "JavaScript Event Handlers".
Like most of the other standard tags, the <frameset> tag honors four of the standard attributes: class, style, title, and id.
Use the class attribute to associate a predefined style class with this frame and, via style inheritance, its content. Alternatively, use the style attribute to define a style inline with the <frameset> tag. We cover styles more completely in Chapter 8, "Cascading Style Sheets".
The id attribute creates a unique identifier for the frame, while title creates a title for the frame that might be presented to the user or used by a nonvisual browser. Section 4.1.1.4, "The id attribute" Section 4.1.1.5, "The title attribute"
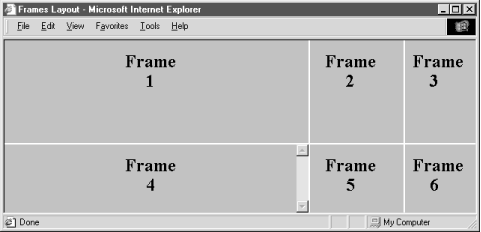
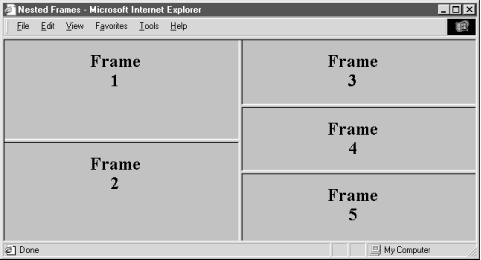
You can create some elaborate browser displays with a single <frameset>, but the frame layout is unimaginative. Instead, create staggered frames and other more complex layouts with multiple <frameset> tags nested within a top-level <frameset> in the frame document (Figure 11-5).
For example, create a layout of two columns, the first with two rows and the second with three rows, by nesting two <frameset> tags with row specifications within a top-level <frameset> that specifies the columns:
<frameset cols="50%,*">
<frameset rows="50%,*">
<frame src="frame1.html">
<frame src="frame2.html">
</frameset>
<frameset rows ="33%,33%,*">
<frame src="frame3.html">
<frame src="frame4.html">
<frame src="frame5.html">
</frameset>
</frameset>

Copyright © 2002 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.